Nestled in the annals of history, the Ottoman Period stands as a testament to the grandeur and complexity of a once-mighty empire. Spanning over six centuries, from the late 13th century to the early 20th century, the Ottoman Empire left an indelible mark on the world, shaping the cultural, political, and economic landscape of its time. In this exploration, we delve into the multifaceted facets of the Ottoman Period, tracing its origins, milestones, and legacy.
Origins and Rise of the Ottoman Empire:
The Ottoman Empire emerged in the wake of the disintegration of the Seljuk Sultanate of Rum in Anatolia. Founded by Osman I in the late 13th century, the Ottomans quickly expanded their territory through strategic military conquests and alliances. The pivotal Battle of Kosovo in 1389 marked a turning point, solidifying the Ottoman presence in the Balkans and paving the way for further expansion.
Golden Age and Splendor:
Under the rule of Sultans like Mehmed II, Selim I, and Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire reached its zenith during the 15th and 16th centuries. This era, often referred to as the Golden Age, witnessed a flourishing of art, architecture, and literature. The architectural marvels of the period, such as the Hagia Sophia and the Topkapi Palace, still stand as iconic symbols of Ottoman opulence.
Militaristic Prowess and Expansion:
The Ottoman military machine was a formidable force, employing innovative tactics and technologies. Janissaries, the elite infantry of the Ottoman Army, played a crucial role in the empire’s military successes. Ottoman expansion reached its zenith with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453, transforming it into Istanbul, the imperial capital.
Cultural and Scientific Achievements:
The Ottoman Empire was a melting pot of diverse cultures and religions. While Islam served as the unifying force, the Ottomans practiced religious tolerance, allowing Christians and Jews to live under the protection of the state. This inclusivity fostered a rich cultural exchange that influenced art, literature, and cuisine. The Ottoman period also saw advancements in science and medicine, with scholars like Ibn Sina making significant contributions.
Decline and Transformation:
As the 17th century unfolded, the Ottoman Empire began to face internal strife and external pressures. Military defeats, economic challenges, and administrative inefficiencies contributed to the decline of the once-mighty empire. The Tanzimat reforms in the 19th century aimed at modernizing the state, but the empire could not escape the geopolitical changes sweeping through the region.
Legacy in the Arab World:
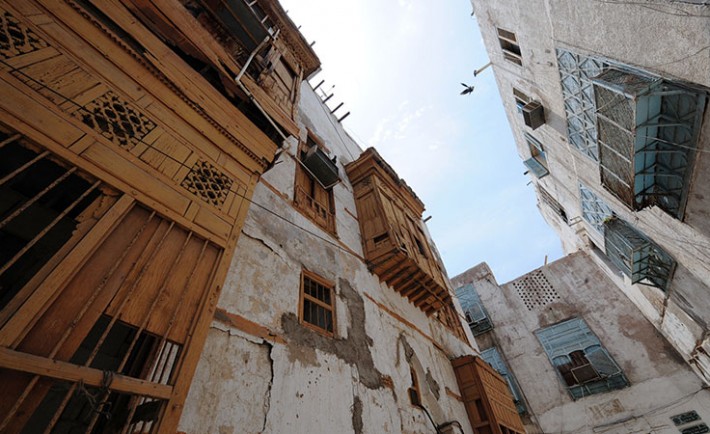
The Ottoman legacy is deeply embedded in the Arab world, including Saudi Arabia. The Ottomans left behind a cultural and architectural imprint that can still be observed in various regions. From the intricately designed mosques to the traditional Turkish baths, the Ottoman influence is an integral part of the cultural mosaic in Saudi Arabia and beyond.
The Ottoman Period, with its ebbs and flows, stands as a rich tapestry woven with threads of conquest, cultural exchange, and innovation. From the rise of Osman I to the transformative reforms of the Tanzimat era, the Ottoman Empire remains a fascinating chapter in world history. As we explore the remnants of this once-great empire in Saudi Arabia, we pay homage to the enduring legacy of the Ottomans and the profound impact they had on the course of history.
More information about the Ottoman Period
Administrative Structure:
The Ottoman Empire boasted a sophisticated administrative system. At its core was the Sultan, considered both the political and religious leader. Below the Sultan were viziers, governors, and local administrators responsible for maintaining order and collecting taxes. The empire was divided into provinces, each governed by a Pasha, who oversaw military, economic, and judicial matters. This hierarchical structure facilitated effective governance across the vast and diverse territories.
Trade and Economic Prosperity:
Trade flourished under the Ottomans, with Istanbul serving as a crucial hub connecting Europe and Asia. The empire controlled key trade routes, fostering economic prosperity. The Grand Bazaar in Istanbul, one of the world’s oldest and largest covered markets, attests to the vibrant commercial activity of the time. Ottoman merchants engaged in trade with various civilizations, contributing to a diverse and cosmopolitan economic environment.
Art and Architecture:
Ottoman art and architecture reflected a fusion of various influences, including Islamic, Byzantine, Persian, and Central Asian. The distinctive Ottoman architectural style is characterized by intricate geometric patterns, domes, and minarets. Notable examples include the Blue Mosque and the Süleymaniye Mosque. Ottoman artists excelled in calligraphy, miniature painting, and ceramics, leaving behind a rich artistic legacy that continues to captivate admirers worldwide.
Social Structure and Daily Life:
The Ottoman social structure was hierarchical, with the ruling class at the top, followed by soldiers, bureaucrats, and artisans. Society was also stratified based on religious affiliations, with Muslims enjoying certain privileges. Family life was central to Ottoman culture, and harems played a significant role. Ottoman cuisine, known for its rich flavors and diverse dishes, reflects the empire’s multicultural influences.
Military Innovations:
The Ottoman military was renowned for its innovative strategies and weaponry. The use of gunpowder, Janissaries armed with muskets, and mobile artillery units gave the Ottomans a technological edge. The Ottoman Navy, led by skilled admirals like Barbarossa, dominated the Mediterranean. The military prowess of the Ottomans played a crucial role in their territorial expansion and long-term dominance.
Religion and Legal System:
Islam was a unifying force in the Ottoman Empire, and the Ottoman legal system was based on Islamic law, known as Sharia. While Muslims adhered to Sharia, non-Muslims were governed by their own religious laws within their communities, under the Ottoman millet system. This system allowed for a degree of religious autonomy and contributed to the overall stability of the empire.
Decline and Legacy:
The decline of the Ottoman Empire was a complex process influenced by internal and external factors. Nationalism, economic challenges, and military defeats contributed to its gradual disintegration. However, the legacy of the Ottomans endures. The establishment of the Republic of Turkey in 1923 marked the end of the Ottoman era, but the cultural, architectural, and historical impact of the empire continues to shape the modern Middle East.
Ottoman Influence in Saudi Arabia:
In Saudi Arabia, the Ottoman legacy is visible in architectural elements, culinary traditions, and cultural practices. The Ottoman influence can be observed in the design of mosques, the use of Arabic calligraphy, and the preparation of dishes that reflect the Ottoman culinary heritage. The historical connections between the Ottoman Empire and the Arabian Peninsula contribute to a shared cultural history that resonates in the region.
In conclusion, the Ottoman Period was a dynamic and multifaceted era that left an enduring imprint on the world. From its administrative innovations to its cultural and artistic achievements, the Ottoman Empire’s legacy is a testament to the complexities of history and the interconnectedness of civilizations. As we explore the remnants of this empire in Saudi Arabia, we embark on a journey through time, unraveling the layers of history that continue to shape our understanding of the past.
Visit Saudi Arabia Destinations Now
Here are some of our Saudi Arabia private tours, offering you the opportunity to embark on a captivating journey through the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Immerse yourself in the rich history of Saudi Arabia as you explore ancient wonders in cities like Riyadh, Jeddah, and Mecca. Discover the archaeological marvels of Al-Ula, with its UNESCO-listed Madain Saleh, and stroll through the traditional streets of Al-Ula Old Town. Experience the highland haven of Abha, nestled in the Asir Province, where you can explore Asir National Park and the historic village of Habala. Take in the breathtaking views at Al-Soudah Park and witness the natural beauty that defines the diverse landscapes of this enchanting kingdom. Whether you’re drawn to the historical charm of Riyadh or the mountainous landscapes of Abha, our Saudi Arabia private tours promise “A Trip to Remember.”

4 Days Riyadh Heritage Tour Package


Saudi Arabia Explorer Riyadh, AlUla and Jeddah – 8 Days

Majestic Tour of Saudi Arabia – 10 Days

How Good are Saudi Arabia Tours?
Saudi Arabia Tours prides itself on being the best travel agency in Saudi Arabia as proven by our numerous positive reviews.
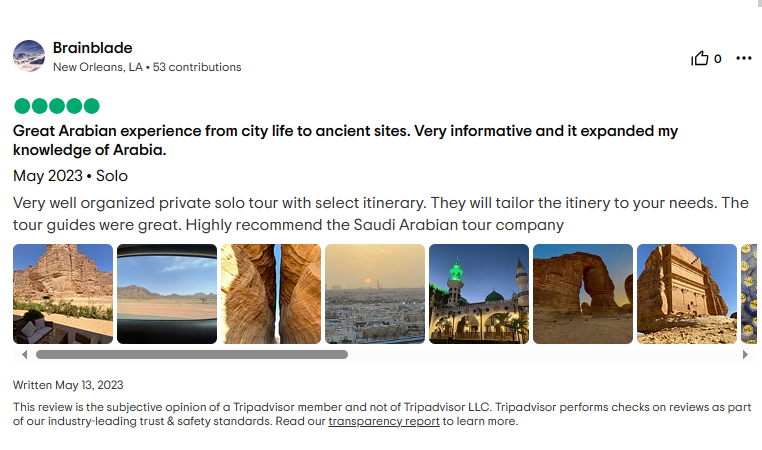
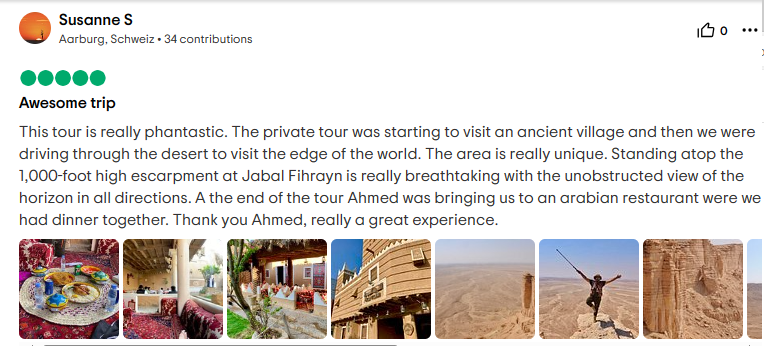
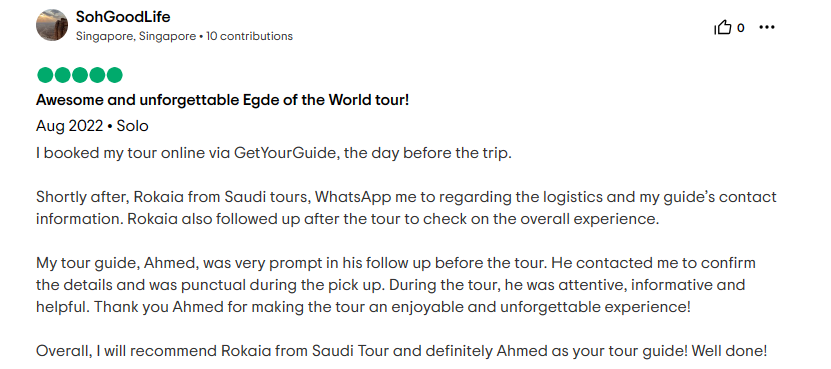
Frequently Asked Questions?
Is Saudi Arabia safe for tourists?
Tourists have been visiting Saudi Arabia and Saudi Arabians have a well-earned reputation for warmth and kindness toward visitors. Saudi Arabia cities are generally very safe, especially in areas where tourists frequent.
How to get a Saudi tourist visa?
Applying for a tourist visa to Saudi Arabia is easy. If you are from one of the 49 eligible countries, you can apply through the eVisa website. Holders of US, UK, or Schengen visas can apply for the visa upon arrival. Saudi Arabia is opening its doors to the world through its new tourist visa. Visitors will have the chance to discover and experience the warm hospitality of the Saudi people, the rich heritage, the vibrant culture, and Saudi Arabia’s diverse and breathtaking landscapes. The visa will be a one-year, multiple-entry visa, allowing tourists to spend up to 90 days in the country.
Are non-Muslims allowed in Saudi?
Non-Muslims can travel to all cities in Saudi Arabia except Medinah and Mekkah, Not allowed to non-Muslims to enter Mecca and Medinah.
Can I wear jeans in Saudi Arabia?
Both men and women are asked to dress modestly in public, avoiding tight-fitting clothing. Women should cover their shoulders and knees in public.
Contact us for more information on:
saudiarabiatours.net@gmail.com
Address: Head Office Olaya St, Riyadh 12213, Saudi Arabia.
If you are booking and taking the tour within 24 hours, or have an urgent request, call us on
Cell/whatsapp : +966558018938 For more info please visit Saudi Arabia Tours

