Saudi Arabia is located on the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East, covering a significant portion of the peninsula’s landmass. Its geographical coordinates range from approximately 23.8859° N latitude to 45.0792° E longitude. To the west, it is bordered by the Red Sea, while the Arabian Gulf (Persian Gulf) lies to the northeast. Saudi Arabia shares land borders with several countries, including Jordan and Iraq to the north, Kuwait to the northeast, Qatar, Bahrain, and the United Arab Emirates to the east, Oman to the southeast, and Yemen to the south. The country has diverse landscapes, including vast deserts, mountain ranges, and coastal areas along the Red Sea and the Arabian Gulf. The Arabian Peninsula is of strategic importance due to its rich energy resources, with Saudi Arabia being a major global exporter of oil.
Saudi Arabia holds significant importance in the Arabian Peninsula for several reasons:
- Economic Powerhouse: Saudi Arabia is one of the largest economies in the region, primarily driven by its vast oil reserves. It plays a crucial role in global energy markets and has considerable influence over oil prices. The revenue generated from oil exports contributes significantly to the country’s economic strength.
- Energy Reserves: The country possesses some of the world’s largest proven oil reserves, making it a key player in the global energy sector. The stability and reliability of Saudi Arabia’s oil production have a direct impact on the stability of the global energy market.
- Islamic Holy Sites: Saudi Arabia is home to two of the holiest cities in Islam, Mecca, and Medina. The annual pilgrimage, known as Hajj, brings millions of Muslims from around the world to these cities. This religious significance grants Saudi Arabia a central role in the Islamic world.
- Political Influence: The Saudi monarchy holds considerable political influence in the region. The country often plays a key role in regional geopolitics, involving itself in diplomatic initiatives and conflicts. Its close ties with other Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries and its alliance with the United States contribute to its political leverage.
- Strategic Location: Geographically, Saudi Arabia occupies a strategic location at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe. Its proximity to key waterways, such as the Red Sea and the Arabian Gulf, makes it a crucial player in regional and international trade.
- Security and Stability: As a major regional power, Saudi Arabia plays a role in maintaining stability in the Arabian Peninsula. The country has a strong military presence and has been involved in regional security initiatives to address common challenges, including counterterrorism efforts.
- Cultural Influence: Saudi Arabia’s cultural and religious influence extends beyond its borders, shaping the cultural practices of Muslims worldwide. The promotion of Islamic values and traditions from Saudi Arabia contributes to its cultural significance in the Arabian Peninsula and the broader Muslim world.
Overall, Saudi Arabia’s economic, religious, political, and strategic importance positions it as a central player in the Arabian Peninsula, with far-reaching implications for the region and the world.
The rich cultural and historical heritage of a society encompasses a tapestry of traditions, customs, art, literature, and milestones that shape its identity over time. This heritage serves as a reservoir of collective experiences, reflecting the evolution and unique character of a community or nation. Whether expressed through ancient artifacts, architectural marvels, oral traditions, or artistic masterpieces, this heritage becomes a living testament to the depth and diversity of human civilization.
Cultural heritage often includes the preservation of language, folklore, rituals, and religious practices, providing a link to the past and fostering a sense of continuity across generations. Historical landmarks, monuments, and archaeological sites stand as tangible evidence of the triumphs, struggles, and innovations that have defined a particular society.
The richness of cultural and historical heritage is not only confined to physical artifacts but also extends to intangible elements such as music, dance, cuisine, and storytelling. These cultural expressions contribute to a shared sense of belonging and contribute to the cultural mosaic that defines a community.
Preserving and celebrating this heritage is crucial, as it allows people to connect with their roots, understand the forces that have shaped their present, and appreciate the diversity that exists within the human experience. Additionally, the study and promotion of cultural and historical heritage contribute to global awareness and foster mutual understanding among different societies.
In essence, a society’s cultural and historical heritage serves as a reservoir of wisdom, a source of inspiration, and a foundation upon which future generations can build their own narratives. It is a valuable asset that requires thoughtful stewardship to ensure its continuity and relevance in an ever-changing world.
Ancient Civilization

Ancient civilizations stand as monumental pillars of human history, showcasing the remarkable achievements, innovations, and cultural legacies of societies that flourished in antiquity. These cradles of civilization emerged independently across different regions of the world, leaving an indelible mark on the collective human experience. From the banks of the Nile to the valleys of Mesopotamia, from the Indus River to the heart of Mesoamerica, ancient civilizations laid the groundwork for the complex tapestry of our modern world.
Pre-Islamic Arabia in Saudi Arabia
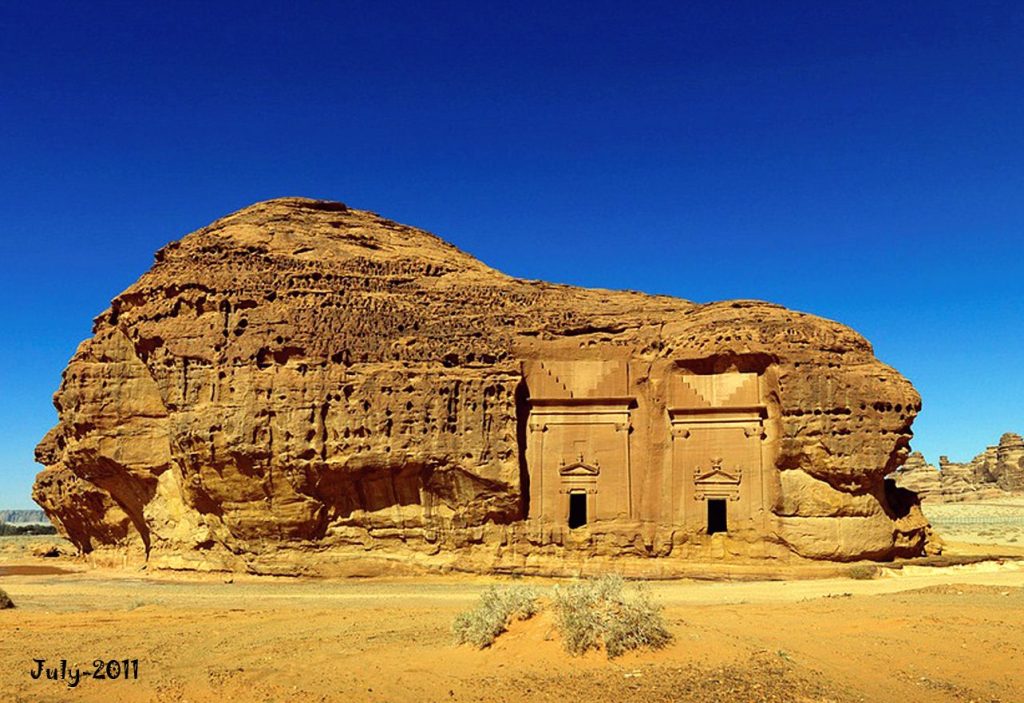

Saudi Arabia, with its vast deserts, ancient cities, and rich cultural heritage, holds a treasure trove of history that predates the advent of Islam. Exploring the epoch known as Pre-Islamic Arabia unveils a captivating narrative of diverse tribes, religious practices, economic activities, and social structures that collectively shaped the foundation of what we now recognize as Saudi Arabia.
Rise of Islam

The Rise of Islam marks a pivotal chapter in the annals of human history, transforming the socio-political landscape of the Arabian Peninsula and beyond. In the early 7th century CE, a revelation from the Prophet Muhammad, as documented in the Quran, ignited a spiritual and societal revolution that would shape the destiny of millions. Emerging from the city of Mecca, Islam swiftly gained momentum, driven by its message of monotheism, justice, and compassion. The Hijra, Muhammad’s migration to Medina in 622 CE, symbolized the establishment of the first Islamic community and laid the foundation for the nascent Muslim society. The subsequent military successes of the Islamic community, combined with the expansion of trade and knowledge, facilitated the spread of Islam across diverse cultures and regions. By the 8th century, Islamic civilization had blossomed into a golden age, fostering advancements in science, art, philosophy, and governance. The Rise of Islam not only transformed the Arabian Peninsula but also left an indelible mark on the global stage, shaping the course of history and influencing the development of diverse civilizations for centuries to come.
Early Caliphates and Dynasties

The Early Caliphates and Dynasties mark a pivotal chapter in Islamic history, shaping the cultural, political, and intellectual landscape of the vast territories under their influence. The period began with the righteous caliphs who succeeded Prophet Muhammad, leading the Muslim community with steadfast commitment and adherence to Islamic principles. The Umayyad Caliphate, established in 661 CE, expanded the Islamic empire, introducing architectural marvels and fostering a golden age of Islamic culture in places like Spain and Syria. The Abbasid Caliphate, emerging in 750 CE, shifted the capital to Baghdad and became a center of learning, where scholars flourished in fields ranging from science and medicine to philosophy and literature. Concurrently, other influential Islamic dynasties like the Fatimids and the Andalusians contributed to the rich tapestry of Islamic civilization. This era witnessed the preservation and translation of classical knowledge from Greek, Roman, and Persian sources, laying the groundwork for the Renaissance in Europe. The Early Caliphates and Dynasties exemplify a period of intellectual enlightenment, cultural flourishing, and expansive Islamic governance that left an enduring legacy on the world stage.
Ottoman Period

The Ottoman Period, spanning from the early 14th century to the early 20th century, marked a transformative and influential era in the history of the Middle East, North Africa, and Southeast Europe. Founded by Osman I in the early 1300s, the Ottoman Empire expanded rapidly, eventually becoming a vast and diverse realm that spanned three continents. At its zenith, under the leadership of iconic figures like Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottomans boasted a sophisticated and multicultural society, fostering advancements in art, architecture, and governance. Istanbul, formerly Constantinople, served as the empire’s majestic capital, showcasing the fusion of Byzantine and Islamic influences. The Ottomans were renowned for their administrative prowess, creating a system that accommodated various ethnic and religious groups within their vast territories. However, as the empire faced challenges and entered a period of decline in the late 17th century, its legacy endured, leaving an indelible imprint on the regions it once ruled. The Ottoman Period remains a pivotal chapter in history, shaping the cultural, political, and architectural landscapes of the modern nations that emerged from its dissolution.
The Founding of Saudi Arabia

The founding of Saudi Arabia is a significant chapter in the nation’s history, marking a transformative period that culminated in the establishment of the modern Kingdom we know today. The story unfolds in the early 20th century when Abdulaziz Al Saud, commonly known as Ibn Saud, embarked on a series of daring campaigns to unify the disparate regions of the Arabian Peninsula. After years of strategic alliances, diplomatic negotiations, and military conquests, Ibn Saud succeeded in consolidating various tribal territories under the banner of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. On September 23, 1932, he formally declared the establishment of the Kingdom, with Riyadh as its capital. This pivotal moment marked the birth of a nation that would go on to play a pivotal role in regional and global affairs. The founding of Saudi Arabia reflects the visionary leadership of Ibn Saud and the resilience of the Saudi people in forging a united and prosperous future.
Rise of the Second Saudi State

The Rise of the Second Saudi State marks a pivotal chapter in the history of Saudi Arabia, unfolding during the early 19th century. Emerging as a direct response to the Ottoman influence and the power struggles within the Arabian Peninsula, the Second Saudi State, led by Imam Turki bin Abdullah, established itself as a formidable force in the region. With its stronghold in Najd, the heartland of the Arabian Peninsula, this period witnessed the expansion of the Saudi influence, driven by a fervent commitment to Wahhabi Islamic principles. The alliance between the House of Saud and the religious leader, Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab, became the bedrock of this resurgence. Together, they forged a political and religious union, seeking to revive the puritanical roots of Islam. The rise of the Second Saudi State not only shaped the internal dynamics of the Arabian Peninsula but also set the stage for the modern Saudi kingdom that would later emerge in the 20th century.
The Modern Kingdom
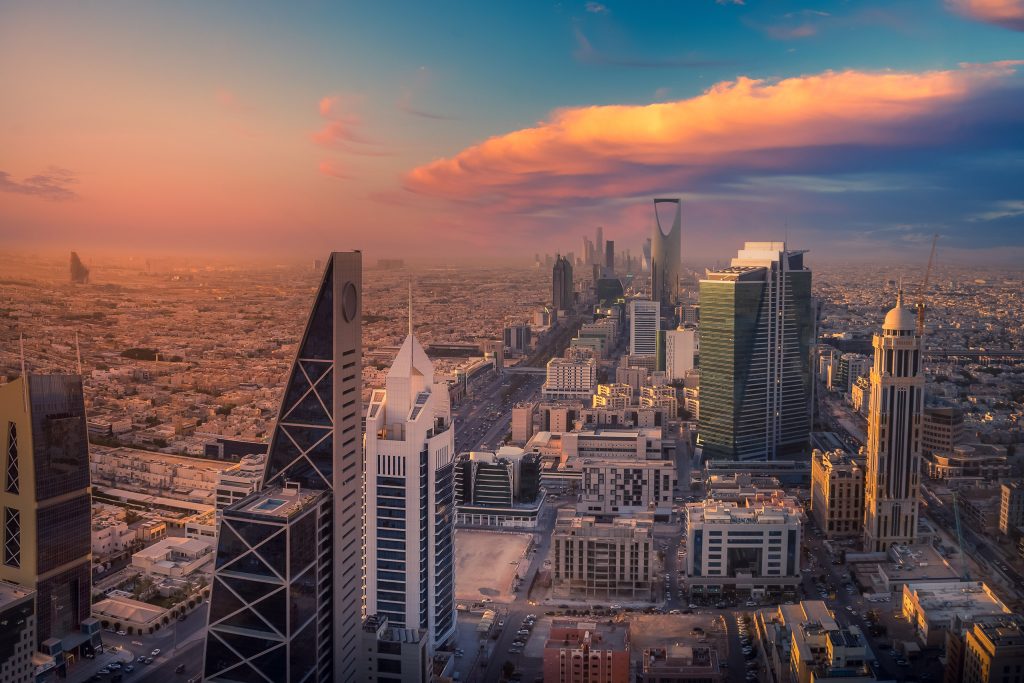

The Modern Kingdom of Saudi Arabia stands as a dynamic blend of tradition and progress, where ancient history converges with contemporary aspirations. Steeped in rich cultural heritage, the kingdom has undergone remarkable transformations in recent decades, positioning itself as a key player on the global stage. Under the Vision 2030 initiative, launched by Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, Saudi Arabia is diversifying its economy, investing in infrastructure, and fostering social reforms. The ambitious project seeks to propel the nation into a post-oil era, fostering innovation, and creating a more inclusive society. Urban centers like Riyadh and Jeddah showcase sleek skyscrapers alongside historic landmarks, embodying the nation’s commitment to preserving its roots while embracing a modern future. As Saudi Arabia opens up to international tourism, visitors can explore not only its ancient archaeological wonders but also experience the vibrant pulse of a society evolving in the 21st century. The Modern Kingdom is a captivating fusion of the old and the new, inviting the world to witness its journey of transformation.
Contemporary Issues

In today’s rapidly evolving world, contemporary issues span a diverse spectrum, reflecting the multifaceted challenges and opportunities we face as a global society. From the ongoing impacts of climate change and environmental sustainability to the intricacies of geopolitical tensions, the current landscape demands our collective attention and thoughtful discourse. Socioeconomic inequality, technological advancements, public health crises, and the pursuit of social justice further contribute to the intricate tapestry of contemporary issues. It is within this dynamic context that we find ourselves navigating the complexities of the digital age, debating the ethics of artificial intelligence, and striving for inclusive and equitable societies. As we grapple with these challenges, it becomes crucial to engage in open dialogue, foster awareness, and seek innovative solutions that pave the way for a sustainable and harmonious future. Exploring these contemporary issues empowers us to be informed global citizens, ready to contribute to positive change and address the pressing concerns that shape our interconnected world.
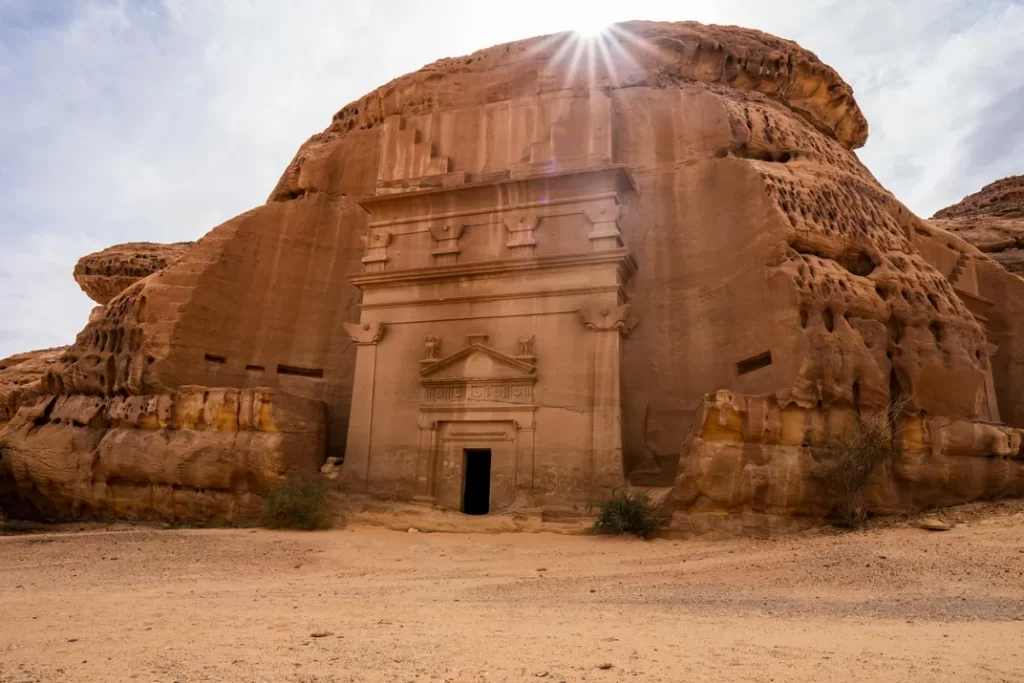
In conclusion, the historical journey of Saudi Arabia is a tapestry woven with rich threads of diverse civilizations and profound transformations. We’ve explored key historical points, from the ancient Nabataean and Dilmun civilizations to the rise of Islam, witnessing the cultural, economic, and religious shifts that have shaped the Arabian Peninsula. Notably, the evolution of Saudi Arabia over time stands as a testament to resilience and adaptability. From the bustling trade hubs of Qaryat al-Faw to the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Madain Salih, the nation has embraced its historical legacy while progressing into the modern era. Crucially, the role of various leaders has been instrumental in steering the country’s destiny. Whether reflecting on the ancient wisdom of Thamud leaders or the contemporary vision of Saudi monarchs, these leaders have played a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s identity, fostering development, and contributing to its prominent stature in the global community. As Saudi Arabia continues to navigate the currents of change, the echoes of its multifaceted past reverberate, providing a foundation for a promising future.
More Topics For The History of Saudi Arabia
The enigmatic ancient civilization of Saudi Arabia has captivated imaginations throughout the annals of history. Its myriad accomplishments in art, culture, and architecture continue to captivate people even in the present day. Here, you will delve into the comprehensive history of this remarkable civilization, exploring the fascinating achievements that have left an indelible mark on the cultural tapestry of Saudi Arabia.
Saudi Arabia
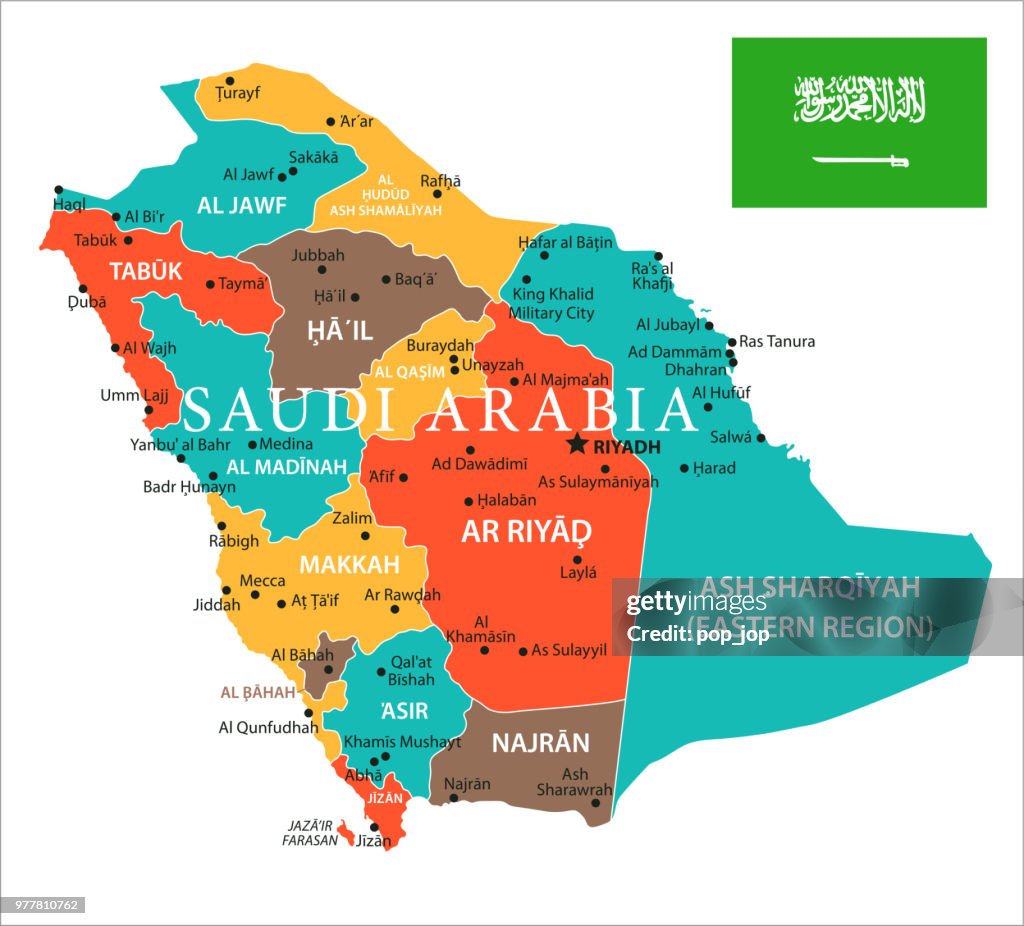
Situated on the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East, Saudi Arabia is a nation steeped in historical significance and characterized by diverse landscapes. Its ancient roots are evident through archaeological findings that highlight civilizations such as Dilmun, Thamūd, the Kingdom of Kinda, and the Al-Magar civilization. The modern era of Saudi Arabia commenced in 1932 when Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman, or Ibn Saud, successfully unified disparate regions through strategic conquests. Reverently known as “the Land of the Two Holy Mosques” due to the sacred sites of Mecca and Medina, the nation holds a central role in the Islamic world. The pivotal discovery of oil in 1938 transformed Saudi Arabia into the world’s second-largest oil producer and exporter, reshaping its economic landscape. Over the years, the Al Saud dynasty has seen a succession of rulers, each contributing to the nation’s growth. In contemporary times, under the leadership of King Salman and Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, Saudi Arabia has embarked on a path of significant transformation, marked by ambitious social and economic reforms encapsulated in Saudi Vision 2030. This nation stands at the intersection of tradition and modernity, embracing a dynamic future while cherishing its vibrant cultural heritage.
Saudi Arabia Leaders

In the heart of the Arabian Peninsula, Saudi Arabia stands as a nation shaped by a succession of leaders whose wisdom, foresight, and strategic prowess have charted the course of the Kingdom’s rich history. From the visionary founder, King Abdulaziz Al Saud, who laid the bedrock of modern Saudi Arabia, to contemporary figures such as Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, orchestrating transformative reforms through Vision 2030, each leader has left an enduring imprint on the nation. This blog endeavors to unravel the narrative of Saudi Arabian leadership, exploring the historical epochs and dynamic shifts that have defined the Kingdom under the stewardship of its monarchs. Join us on a journey through time, where leadership transcends mere governance and becomes the compass guiding Saudi Arabia through the complexities of tradition, modernity, and global dynamics.
Saudi Customs And Traditions
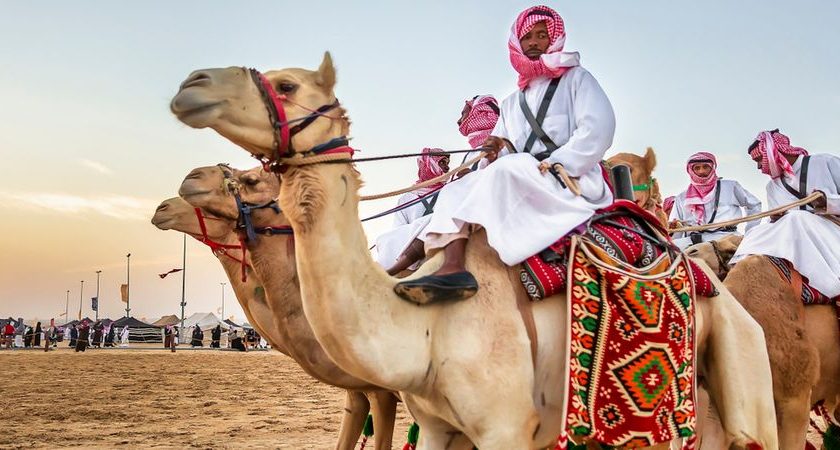

In the heart of the Arabian Peninsula lies Saudi Arabia, a nation steeped in rich history, diverse landscapes, and a tapestry of customs and traditions that echo through the ages. As one delves into the vibrant cultural fabric of Saudi Arabia, a world unfolds where ancient traditions seamlessly coexist with the dynamism of the modern era. The customs and traditions of Saudi Arabia are not merely rituals; they are intricate threads weaving together the past, present, and future of a society deeply rooted in its values and heritage. From the majestic Arabian deserts to the bustling cityscapes, Saudi customs and traditions provide a captivating lens through which to explore the essence of this nation, where time-honored practices stand as pillars of identity and resilience in the face of a rapidly changing world.
Best Holidays to Saudi Arabia
Are you in search of the ideal Saudi Arabia Holiday Packages? Saudi Arabia Tours provides you with the opportunity to explore the marvels of Saudi Arabia, from its majestic landscapes to the rich historical and cultural heritage in cities like Riyadh, Jeddah, Mecca, and Medina. Choose from a diverse range of customized tours and holidays designed to cater to every preference. Select your preferred holiday package and embark on your dream vacation now!

4 Days Riyadh Heritage Tour Package


Saudi Arabia Explorer Riyadh, AlUla and Jeddah – 8 Days

Majestic Tour of Saudi Arabia – 10 Days
How Good are Saudi Arabia Tours?
Saudi Arabia Tours prides itself on being the best travel agency in Saudi Arabia as proven by our numerous positive reviews.
Frequently Asked Questions?
Is Saudi Arabia safe for tourists?
Tourists have been visiting Saudi Arabia and Saudi Arabians have a well-earned reputation for warmth and kindness toward visitors. Saudi Arabia cities are generally very safe, especially in areas where tourists frequent.
How to get a Saudi tourist visa?
Applying for a tourist visa to Saudi Arabia is easy. If you are from one of the 49 eligible countries, you can apply through the eVisa website. Holders of US, UK, or Schengen visas can apply for the visa upon arrival. Saudi Arabia is opening its doors to the world through its new tourist visa. Visitors will have the chance to discover and experience the warm hospitality of the Saudi people, the rich heritage, the vibrant culture, and Saudi Arabia’s diverse and breathtaking landscapes. The visa will be a one-year, multiple-entry visa, allowing tourists to spend up to 90 days in the country.
Are non-Muslims allowed in Saudi?
Non-Muslims can travel to all cities in Saudi Arabia except Medinah and Mekkah, Not allowed to non-Muslims to enter Mecca and Medinah.
Can I wear jeans in Saudi Arabia?
Both men and women are asked to dress modestly in public, avoiding tight-fitting clothing. Women should cover their shoulders and knees in public.
Contact us for more information on:
saudiarabiatours.net@gmail.com
Address: Head Office Olaya St, Riyadh 12213, Saudi Arabia.
If you are booking and taking the tour within 24 hours, or have an urgent request, call us on
Cell/whatsapp : +966558018938 For more info please visit Saudi Arabia Tours

